JEE Mains 2024 Kinematics Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Preparing for JEE Mains 2024? Strengthen your understanding of kinematics with these previous year questions (PYQs). Dive into these problems, solve them, and enhance your problem-solving skills for the exam.
Particle in Circular Motion with Uniform Speed:
A particle moving in a circle of radius R with uniform speed takes time T to complete one revolution. If this particle is projected with the same speed at an angle θ to the horizontal, the maximum height attained by it is equal to 4R. The angle of projection θ is then given by?
2. One-Dimensional Motion with Variable Force:
A particle is moving in one dimension (along x-axis) under the action of a variable force. Its initial position was 16 m right of origin. The variation of its position (x) with time (t) is given as x = -3t³ + 18t² + 16t, where x is in meters and t is in seconds. What is the velocity of the particle when its acceleration becomes zero?
3. Relative Velocity of Trains:
Train A is moving along two parallel rail tracks towards the north with a speed of 72 km/h and Train B is moving towards the south with a speed of 108 km/h. What are the velocity of Train B with respect to Train A and the velocity of the ground with respect to Train B (in m/s)?
- (1) -30 and 50
- (2) -50 and -30
- (3) -50 and 30
- (4) 50 and -30
4. Particle Starting from Rest with Varying Velocity:
A particle initially at rest starts moving from the reference point x = 0 along the x-axis, with a velocity v that varies as v = 4/x m/s. What is the acceleration of the particle in m/s²?

5. Ant's Position in Y-Z Plane:
The position of an ant (S in meters) moving in the Y-Z plane is given by S = 2t²j + 5k (where t is in seconds). What is the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the ant at t = 1 s?
- (1) 16 m/s in the y-direction
- (2) 4 m/s in the x-direction
- (3) 9 m/s in the z-direction
- (4) 4 m/s in the y-direction
6. Particle with Constant Acceleration in X-Y Plane:
A particle starts from the origin at t = 0 with a velocity of 5i m/s and moves in the x-y plane under the action of a force which produces a constant acceleration of (3i + 2j) m/s². If the x-coordinate of the particle at that instant is 84 m, what is the speed of the particle at this time (√a m/s)? Find the value of a.
7. Body Falling Under Gravity:
A body falling under gravity covers two points A and B separated by 80 m in 2 seconds. What is the distance of the upper point A from the starting point (use g = 10 m/s²)?
g
8. body starts moving from rest with constant acceleration covers displacement S₁ in first (p-1) seconds and S₂ in first p seconds. The displacement S₁ + S₂ will be made in time:
(1) (2p+1) s
(2) √(2p² - 2p + 1) s
(3) (2p-1) s
(4) (2p² - 2p + 1) s
9. Ball Rolling Off a Stairway:
A ball rolls off the top of a stairway with a horizontal velocity u. The steps are 0.1 m high and 0.1 m wide. What is the minimum velocity u with which the ball just hits the step 5 of the stairway (√x m/s where x = _______)? Use g = 10 m/s².

10. Particle's Position and Velocity in a Straight Line:
A particle is moving in a straight line. The variation of position 'x' as a function of time 't' is given as x = (t³ - 6t² + 20t + 15) m. What is the velocity of the body when its acceleration becomes zero?
- (1) 4 m/s
- (2) 8 m/s
- (3) 10 m/s
- (4) 6 m/s
11. Displacement and Velocity Increase of a Particle:
The displacement and the increase in the velocity of a moving particle in the time interval of t to (t + 1) s are 125 m and 50 m/s, respectively. What is the distance traveled by the particle in the (t + 2)ᵗʰ second?
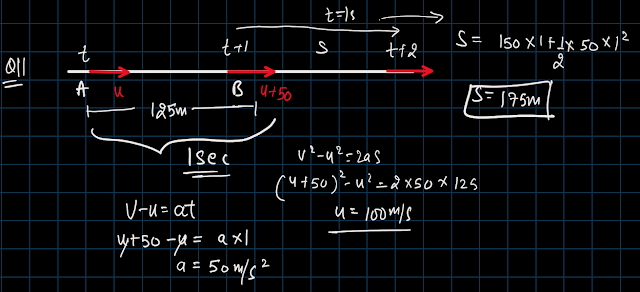
12. Projectile Motion from a Tower:
Projectiles A and B are thrown at angles of 45° and 60° with the vertical respectively from the top of a 400 m high tower. If their time of flight is the same, what is the ratio of their speeds of projection VA: VB?
- (1) 1:√3
- (2) √2:1
- (3) 1:2
- (4) 1:√2
13. Relation Between Time, Distance, Acceleration, and Velocity:
The relation between time 't' and distance 'x' is t = αx² + ẞx, where α and ẞ are constants. What is the relation between acceleration (a) and velocity (v)?
- (1) a = -2αv³
- (2) a = -5αv
- (3) a = -3αv²
- (4) a = -4αv


















-min.png)





