⚙️ Work, Energy & Power – Chapter Notes for JEE/NEET 2025 🔋
📝 Preparing for JEE or NEET and have “Work, Energy & Power” on your revision list? Here are complete chapter notes covering definitions, core formulas, typical problem types, and handy tips for solving related numerical problems quickly and accurately. Save time and boost your concepts with this one-stop summary! 💡
PDF IS AVAILABLE IN THE END OF THIS NOTES
Work :-
• When a body moves through a certain distance in any direction under the influence of an applied force except the direction perpendicular to the direction of a platform force .
• It is scalar quantity and scalar or dot product .
 |
| Work done |
Work done in component form :-
 |
| Workdone in component form |
Work done for constant and variable forces :-
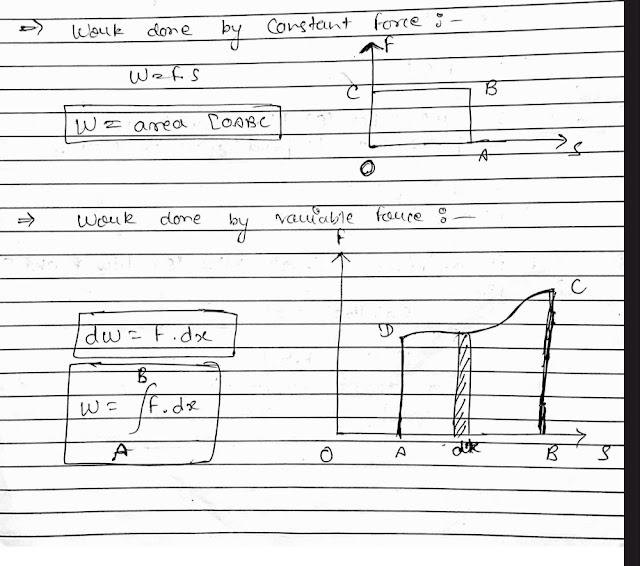 |
| Workdone by constant and variable forces |
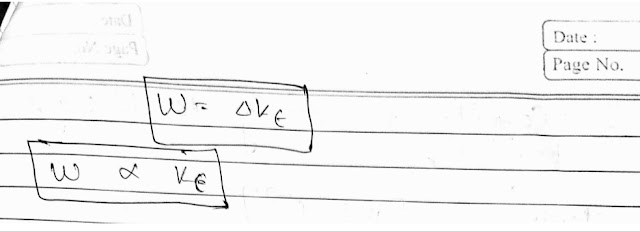
# Work Enegry theorem for constant force :-
 |
| Work Enegry theorem |
# Work Enegry theorem for variable force :-
 |
| Work Enegry theorem |
Power :-
Time rate at which work is done or rate of doing work is known as power .
 |
| Power |
Enegry :-
Capacity or ability to do work by a body .
Unit:- Joule
=> Kinetic energy :-
• It is the enegry which possessed with motion .
• Non - Conservative force
 |
| Kinetic Enegry |
# Relation between Kinetic energy and Linear momentum :-
 |
| Relation b/w Kinetic energy and momentum |
=> Potential Energy :-
• It is the enegry which is possessed with position .
• Conservative Force
=> Two important types of potential energy :-
1. Gravitational Potential Energy :-
It is the energy possessed by the body of its position above the surface of the earth .
 |
| Potential Energy |
2. Elastic Potential Energy :-
 |
| Elastic Potential Energy |
Note:-
• Spring of greater force constant 'k' said to be 'stiffer' .
• spring of smaller force constant 'k' said to be 'soft' .
# Spring potential Energy, Work Enegry theorem :-
 |
| Spring potential Energy |
 |
| Workdone by spring force |
Concept of conservative and non conservative :-
=> Conservative Force :-
A force is conservative when workdone bh the net force on a moving particle between the particles initial and final position.
Examples :- • Gravitational force
• Spring Force
• Potential Energy
=> Non Conservative :-
A force is non conservative when the work done by this is dependent on the path being follow the particle are called non conservative force .
Examples :- • Force of friction
• Kinetic energy
Mechanical energy :-
The mechanical energy of a body is the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy .
 |
| Mechanical energy |
# Illustration of law of conservation of mechanical energy :-
 |
| Conservation of Mechanical energy |
Collisions :-
1. Elastic collision :-
• A collision in which there is no loss of kinetic energy is called elastic collision .
• kinetic energy is conserved
• Linear momentum
• Total energy is conserved
• The force must be conservative force .
• Practically, there won't be no perfect elastic collision.
2. Inelastic collision :-
•A collision in which there is same loss of kinetic energy is called in elastic collision .
• Linear momentum is conserved .
• Kinetic energy is not conserved .
• Total energy is not conserved .
• Force must not be conservative .
• Practically there won't be no perfect inelastic .
Elastic Collision in 1-D ( dimension)
 |
| Elastic Collision in 1D |
Inelastic Collison in 1-D(dimension)
 |
| Inelastic Collison in 1D |
 |
| Kinetic energy is not conserved in inelastic Collison |
Elastic Collision in 2-D(dimension)
 |
| Elastic Collision in 2D |
✅ Final Tip: Revise these notes daily and solve one problem every day to build clarity and speed. Found this helpful? 🤝 Bookmark, share, and comment below with any doubts!
Click here Notes for pdf










-min.png)





